Introduction to Fundamental Analysis
In terms of predicting price movements and identifying Forex trading opportunities, there are two main approaches. One of them is technical analysis, which attempts to predict the direction a price is taking based on historical price data and statistics.
The other main approach is performing a fundamental analysis which, as its name suggests, is based on taking into account the economic fundamentals of a given asset, sector, or economy to determine whether it is currently being traded higher or lower than its actual “fair price”, assuming that eventually the price will reflect this information. In other words, the main goal is establishing, based on publicly available data, whether the asset is undervalued, overvalued, or priced “correctly”.
Another way of seeing it involves understanding that the Forex market is driven by supply and demand, and that the fundamental approach aims for understanding the factors that affect supply and demand for profit-making purposes.
Fundamental trading is a very popular method, though it is often linked to buy-and-hold strategies instead of short-term trading. Some of the greatest investors, like Warren Buffet and Benjamin Graham, often make their investment decisions based on fundamentals.
Stock traders usually base their fundamental assessments on the financial statements of the company they are valuing. This allows them to determine whether it is appropriate to sell or to buy a particular stock.
It is also possible to adopt this approach when it comes to performing an analysis of the currency markets. Just as the financial statements of a given company can be used to determine whether its stocks are trading higher or lower than the “fair price”, economic indices (which help to measure the economic performance of a country) can help to determine whether a given currency is overpriced or not, or predict which direction the markets could take after its publication or even over the longer run.
There are some factors that have to be considered before beginning to explore this approach. Firstly, some of the relevant economic indices have more impact on the performance of a currency than others, this implies that the publication of certain indices or figures is more prone to having a bigger influence in the markets than the publication of any other relevant information or event. Furthermore, the markets often move on expectations for the future, so the criteria and the anticipation of the experts and analysts regarding any economic figure or event can end up being relevant before and after the information is released or the event occurs.
Therefore, a trader that is interested in adopting this approach should not only pay attention to the figures and events themselves, but also to analysts' forecasts, as the expectations could affect the market's reaction in a significant way.
Fundamental Case Study: the U.S. Dollar
Let us take the U.S. dollar as an example. The U.S. dollar is the official currency of the United States, which implies that its performance is supposed to be intrinsically linked with the state of the US economy and the expectations for it. And not only that, the dollar’s price behavior is also highly susceptible to events that are not necessarily related to the United States itself: any specific event or data that is relevant to other currency could drive traders towards the U.S. dollar, being the main competitor of some of the most important currencies (like the euro or the yen) and a well-known safe haven asset.
In terms of relevant figures and indices, there are several that are regularly published by both the United States government as well as private organizations. An example of this is the Consumer Price Index (better known as CPI or the inflation rate) which is published by the U.S. Department of Labor Statistics and is used to estimate whether the country is going through an inflationary or a deflationary period.
Regardless of any personal opinion an individual trader may have in terms of interpreting what this figure means for the economy of the United States, a decreasing CPI is usually perceived as a positive signal by the markets, and vice versa.
Market expectations for the CPI itself often end up affecting the performance of the currency. Because of this, it is usual to find out that the publication of any figure has already been priced in by the markets.
This is why sometimes markets do not seem to react as expected right after a significant event or announcement, as sometimes the event itself is quite predictable and was already assimilated by traders. Furthermore, sometimes the predictions turn out to be inaccurate, which can cause an unexpected reaction in the markets.
For example, if the Federal Reserve announced an unexpected rate cut this would likely drive investors to sell their dollar-denominated assets, which could put a significative downward pressure on the dollar right after the announcement. Otherwise, they would have already taken this outcome into consideration, which would not have caused such a dramatic reaction.
Just as the Consumer Price Index and the interest rate can be important pieces of information for an experienced trader, there are several other economic indicators and events that can be relevant for the performance of a given currency. The non-farm payrolls figure, among other economic indicators, comes to mind in the case of the U.S. dollar.

Some of them tend to signal the actual state of the economy, such is the case of the unemployment rate and the gross domestic product figures. While others might just boost or hinder the expectations about the future, interest rates announcements come to mind as an example, as well as any announcement or statement made by government or central bank officials.
This applies to other currencies as well. An increasing eurozone Consumer Price Index tends to have a negative effect on the euro’s performance, while a positive assessment of the eurozone economy by the European Central Bank president may boost it.
The Forex Economic Calendar
Considering that it is usually very hard to keep track of all the relevant information pertaining to any specific currency when engaged in currency trading, the need arises for an efficient way to do so. While this information can be accessed easily from many news outlets, it may be more convenient to have access to automatic updates. Many Forex brokers and news sites provide access to one.
A typical economic calendar not only provides key real-time information related to the most popular currencies, but also provides the trader with information about any upcoming relevant event that may influence the markets, the analysts’ expectations, previous figures and even the likely degree of impact of the information that is being reported.
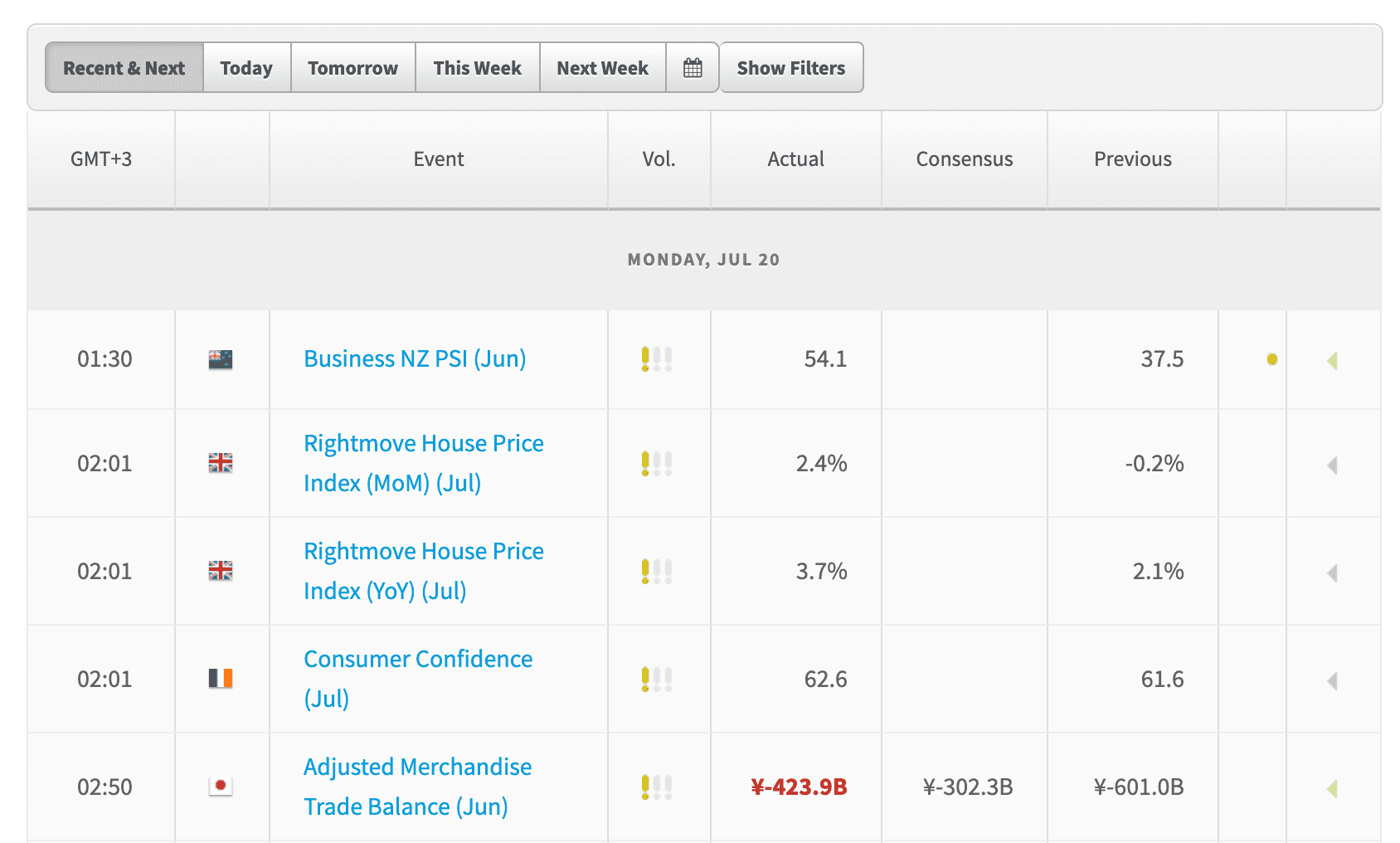
Most Economic calendars can be customized to only show the information that the trader considers relevant. For example, if a trader is interested on trading the EUR/JPY pair he or she could filter the calendar so only relevant information regarding the euro and the Japanese yen appears.
Using the data provided by the economic calendar, an investor can determine whether a specific currency has strong or weak fundamentals, which would help him to decide whether he should buy, sell, or hold it.
An alternative or adjacent method to using an economic calendar and to relying on your own fundamental assessments is basing your strategies on the perception of a third party. Some news sites, trading platforms and brokers provide their own fundamental assessments to their clients, so learning how to read fundamental analysis in forex and relying on their insights can be a viable option.
Making and Applying a Fundamental Analysis
List all the currencies your Forex broker offers for trading. Look for recent data on those currencies that may influence their behavior in an economic calendar. The gross domestic product and the interest rate are an example of commonly employed data to perform fundamental analysis.
It is important to consider the actual figures as well as the market consensus forecasts, which are also available on any regular economic calendar. This data can be used to analyze and compare the trends and to ascertain if the actual figures were in line with the expert forecasts. This last step is important since the impact of the publication of the economic data depends on whether the information was unexpected by the markets: if the figure remains in line with the market consensus, then the impact of its publication will be relatively lower as probably at that point the information would have been already priced in the markets.
For example, if the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis reports that the United States GDP increased on the past quarter, this would be obviously a bullish sign as it signals strong fundamentals. However, if the figure remained in line with the analysts forecasts it’s highly likely that this data was already priced in the markets, so at the moment of its publication the positive impact of this information on the dollar performance could be lower than if the data came in much higher than expected.
It is important to remark that the analysis could be way more effective if historical data, which is also available on the regular economic calendar, is used. In this case, the historical data can be used to determine whether the US economic performance is on an upwards trajectory, which is a sign of a strongly growing economy.
It is better to complement your analysis using other relevant economic information, such as the inflation level, or the manufacturing PMI. For example, a rising manufacturing PMI would back up the case for a strongly growing US economy, aiding the bullish position, on the other hand, a negative figure could weaken your assessment, which may be a sign to rethink your strategy.
Using this approach, you can classify all currencies into three main groups:
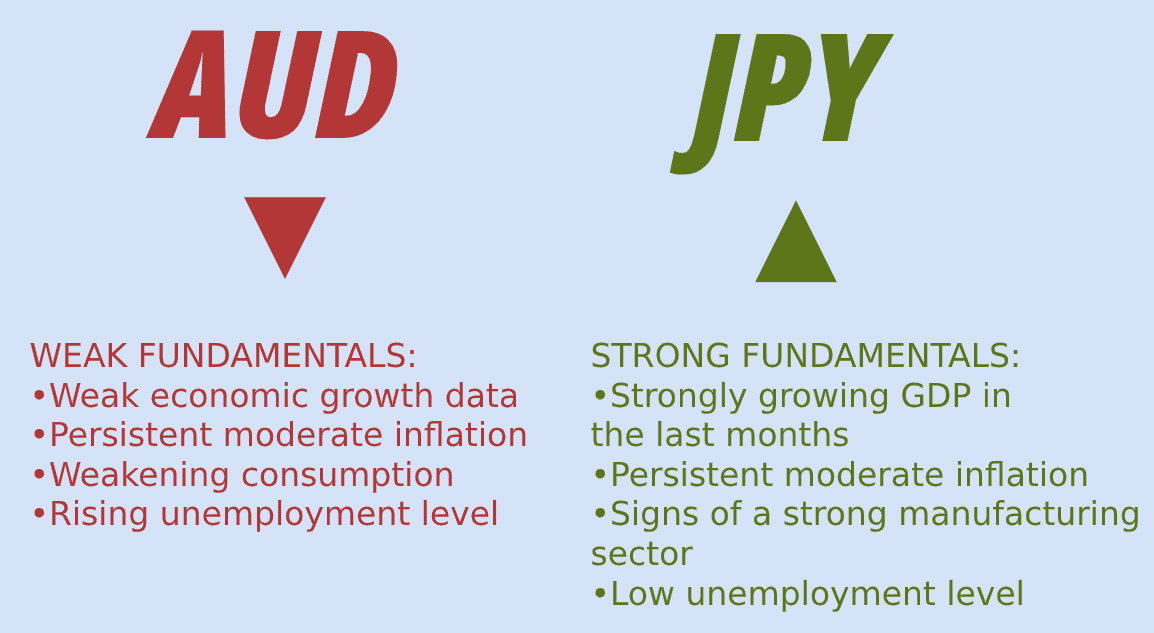
- Currencies with strong fundamentals: this suggests you should be bullish on this currency.
- Currencies with weak fundamentals: this suggests you should be bearish on this currency.
- Currencies that are a mixture: this suggest you should either avoid (at least for now) or just be neutral about trading this currency.
If a specific currency has strong fundamentals, while one of its competitors does not, the common approach is selling the currency with weak fundamentals against the one with bullish fundamentals. For example, if your analysis suggests that you should be bullish on the Japanese yen and bearish on the Australian dollar, then you should sell AUD/JPY.
Trading with Fundamentals: A Warning
Fundamental trading can be a very powerful method to make money in the markets, especially if coupled with strategies that are based on technical analysis.
However, you have to realize that the markets may not react the way you expect after the release of economic data, even if its meaning seems unambiguously positive or negative. As we already mentioned, sometimes the markets already priced the event, or decide to interpret the data in another way. For example, an overly positive unemployment figure could be interpreted as a sign of the possible stagnation of the job market, or any other relevant piece of data that is not positive (for example, lower average earnings) could be released at the same time and attract the market’s attention.
FAQs
How do you conduct a fundamental analysis in Forex?
The best method to perform fundamental analysis in forex is by keeping an economic calendar on hand with all the relevant past and future information about the currencies you are trading. Special attention should be paid to events that are listed as high impact.
How do you read a fundamental analysis?
Monitor the changes over time of a currency’s country’s major economic variables, such as GDP, inflation (CPI), and the rate of interest. Compare the recent numbers here also to what the forecasts were. If data is getting better and beating the forecasts, then the fundamentals suggest the currency should be getting stronger.
What are fundamentals in Forex?
Fundamental analysis in forex implies identifying the fundamental value of a currency. Several economic indicators can be used to do so, such as the job markets indicators, the Gross Domestic Product, among others.
What is technical and fundamental analysis in Forex?
Technical analysis is a method for predicting price movements of a given currency based on statistical trends and historical data.
Fundamental analysis tries to do the same, but as its name suggest, it is based on the fundamentals of a currency.
